Despite scrutiny over hedge resources’ underperformance since the financial meltdown, huge university endowment resources that way of Northwestern University remain holding on to — or even raising — their particular stakes in “alternative investments, ” which are generally at risk of high risk but often do much better than equities.
Despite scrutiny over hedge resources’ underperformance since the financial meltdown, huge university endowment resources that way of Northwestern University remain holding on to — or even raising — their particular stakes in “alternative investments, ” which are generally at risk of high risk but often do much better than equities.
Under the backdrop of soaring global equities areas and still stagnating rates of interest, Northwestern University’s endowment achieved a lofty return of 16.8 percent when you look at the financial year finished August 31, 2014, during which the marketplace value of the main fund grew by a historical level of 24 % to $9.7 billion. The fund is currently the 8th largest university endowment by web assets in the united kingdom.
Endowments collect and spend money or any other monetary possessions contributed into the university. Like many institutional investors, institution endowments run in long-time perspectives and strive for inflation-adjusted returns that go beyond stock exchange indexes and institution investing requirements. With a diverse assortment of techniques and asset courses, endowments set-out strict asset-allocation groups which are meant to attain the best comes back.
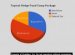
Since the termination of August, the hedge investment portfolio of Northwestern’s endowment makes up virtually 18 per cent of fund. With a robust 11 per cent return, its hedge funds this past year outperformed a benchmark portfolio by 4 percentage points, the best outperformance across all seven asset courses that investment invests in.
The endowment produces a unique benchmarks that represent a diverse world or “opportunity set” of every asset class. For hedge resources, the standard weights equity and hedge investment indices by the fund’s experience of each strategy.
“Over the last year and a half we've relocated to an over weight in our hedge fund portfolio, as before that people were underweighted, ” said William McLean, main investment officer of Northwestern University’s endowment, in a job interview. “So there’s absolutely already been a conscious energy to consider some uncorrelated strategies that don’t relate to equities markets’ increasing.”
The share of hedge funds into the endowment happens to be underneath the U.S. university-endowment average since 2004. The allocation peaked in both financial 2003 and 2004 at 20.4 per cent and dropped to a trough of 14.6 per cent in 2011.
Since 2011 McLean’s team has been plowing more income to the hedge investment profile due to the considered growth potential — the portfolio’s return grew from 1.2 percent in 2009 to 11 per cent just last year, where time its yearly gain ended up being over the standard the investment office updates annually.
This portfolio performance stands out at any given time when the hedge investment business is faltering.
Considering that the financial meltdown, the hedge fund industry in general is underperforming the stock market, measured by the traditional & Poor’s 500 stock list, yearly. The bottom was at 2013, when hedge funds yielded a 9.13 % return as measured by the HFRI index compiled by Chicago-based Hedge Fund Research Inc., compared with the market’s 32 % gain.
Some institutions have finally lost patience with hedge resources.
CalPERS’ about $4 billion hedge funds and hedge fund-of-funds constituted no more than 1.3 % of its a lot more than $300 billion assets. But its complexity and high expense yet reduced return relative to CalPERS’ dimensions, according to CalPERS’ main financial investment officer, were the causes for losing this sophisticated profile.
But the hedge fund industry’s disappointing post-financial crisis performance will not concern McLean a lot. He still matters on hedge funds to lead Northwestern’s endowment upward.
 “It doesn’t worry me personally, ” McLean claimed. “The explanation you have got hedge resources is the fact that, ideally, they will protect you if you have large correlation [with the stock exchange.] Hedge resources have historically delivered for all of us everything we desire ultimately, which is investing plus rising prices, call it roughly 8 percent. It is anything to counterbalance the equity market volatility, along with still the chance to have good comes back.”
“It doesn’t worry me personally, ” McLean claimed. “The explanation you have got hedge resources is the fact that, ideally, they will protect you if you have large correlation [with the stock exchange.] Hedge resources have historically delivered for all of us everything we desire ultimately, which is investing plus rising prices, call it roughly 8 percent. It is anything to counterbalance the equity market volatility, along with still the chance to have good comes back.”
In 2008, McLean remarked when you look at the endowment’s economic report from the verge associated with the financial crisis: “The Investment workplace believes that long-term customers for growth in globally financial areas are now being masked by turmoil, anxiety, and uncertainty, hence the share has many possibilities in that environment.”
Northwestern’s endowment quickly restored from crisis by coming back 10.8 % in 2010, when its hedge resources yielded 15.5 %.
The outperformer
Regarding the endowment’s recent outperformance, McLean attributed the success to your variety of distinguished legacy fund managers, always moderated by his team’s constant work to help keep the endowment adequately fluid.
The financial investment office presently outsources about 95 per cent for the fund to outdoors supervisors, and manages in-house just the fixed income portfolio, a modest asset course the endowment keeps as an “anchor” or safety net in case of deflationary events.
The group divides its hedge investment portfolio into three methods. The long/short equity method, that used to account for 1 / 2 of the asset course before 2010, has shrunk to 40 %. “Event-driven, ” which occupies about 20 % associated with portfolio, in addition shrank after 2010.
The “uncorrelated methods, ” an accumulation of strategies with “very reasonable correlation to equity areas, ” ended up being added to the portfolio in 2010, McLean stated. This 3rd method today is the reason the remaining 40 percent of hedge resources.
“[The distribution] is an expression of the kinds of legacy supervisors we've in the portfolio, ” McLean explained. “We had been mostly long/short before, after that we'd some liquidity coming to the portfolio, and we’ve taken that opportunity to add even more returns uncorrelated [to the equity market.] ”
Some marketplace watchers say the hedge fund complex has actually eventually been hitting straight back since the start of 2015. Information from HFR suggests that in the first quarter hedge funds beat their particular equity alternatives, assessed because of the S&P 500, the very first time in six years.
The Yale design
Ken Redd, manager of research and policy evaluation at the National Association of university and University company Officers, recalled that 2014 was a particularly good year for endowments purchased exclusive equities, specially with venture capital getting a sturdy 22 percent.
Yale devoted 33 per cent of their $24 billion endowment to personal equity, when compared to university-endowment average 10 % allocation.
Personal equities account for roughly one fifth of Northwestern’s endowment. Despite earning a lofty 28.2 per cent return out of this asset class a year ago, McLean has no want to expand the fund’s allocation to this asset class.
“We are pretty comfortable where we are now, ” McLean stated.
Redd said Northwestern’s security in allocating assets is typical across college endowments of most sizes.
Consistently before ten years, about 60 to 65 per cent associated with larger-endowment assets are typically in alternate possessions, which include hedge funds, exclusive equity and derivatives, Redd said. Large endowments are particularly attracted to legacy fund managers across alternative investment strategies, whereas for smaller endowments, only about 35 to 40 percent is devoted to these riskier yet often more rewarding assets.
Huge endowments tend to be less likely to want to make radical changes, largely because of their longer time perspectives and large exposures to alternate asset classes, which often require holding durations of five to ten years.