 Like Ol' blue-eyes and ny, ny, hedge resources and private equity are often pointed out in identical breath. Certain, both investment kinds are sold through personal choices that depend on exemptions from registration. And both tie-up people' money for extended than shares or ETFs in exchange for the chance to generate better-than-market returns. But there are much more variations than similarities between these two kinds of funds. People should be aware of the ramifications with their portfolios.
Like Ol' blue-eyes and ny, ny, hedge resources and private equity are often pointed out in identical breath. Certain, both investment kinds are sold through personal choices that depend on exemptions from registration. And both tie-up people' money for extended than shares or ETFs in exchange for the chance to generate better-than-market returns. But there are much more variations than similarities between these two kinds of funds. People should be aware of the ramifications with their portfolios.
1. Just what was I purchasing right here?
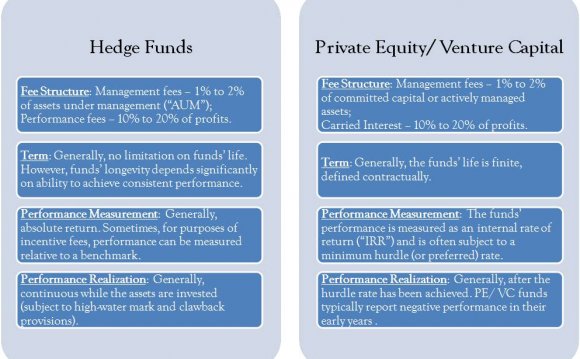
Most hedge resources spend money on securities like shares, bonds, types and commodities which are tradeable in the open market and that can be purchased or obsessed about brief notice. Positions inside portfolios among these funds change usually, often even on an intraday foundation.
Exclusive equity funds, in contrast, invest in organizations or properties using the intent to operationally manage, develop and finally offer these assets. All investments commonly take 3-5 years, and often much longer, to be fully realized.
2. Can it be an investment or a commitment?
Once you spend money on a hedge investment, your cash renders your bank account as straight away as when you invest in a shared fund. Which can be as you would anticipate, since the greater part of hedge fund managers are constantly deploying money in (mainly) marketable securities that trade in real time.
Subscribe to a private equity fund, conversely, and you usually cannot need to make an instantaneous debit from cost savings. Instead, could devote some money become compensated to the fund as needed for discounts the profile managers hit in the personal markets. As much as investors may want transparency in to the time of the capital calls, funds often just don't know the timing when you subscribe. Financial investment opportunities can arise unpredictably, and also deals which were in a fund's pipeline for months or many years could possibly get delayed or accelerated due to the fact exchanging events total their particular negotiations.
3. The length of time does the dedication last?
Exclusive equity funds lack a limitless time frame to ask your committed capital. Instead, they've an investment period that's written to the investment's offering documents. It really is generally speaking 3-5 years, after which the investment must launch you from your commitment, “use it or lose it” style.
The rest for the fund's life is the harvest duration, where the fund comes back arises from opportunities. Some exclusive equity resources are able to re-call a portion for the proceeds they come back to you in order to make investments in new profile businesses. This capability is named recycling. A recycling provision can lengthen the period of investment substantially, which may never be desirable from a liquidity perspective but can produce interesting financial investment possibilities and increase the percent of capital commitment this is certainly actually placed to exert effort.
Since hedge resources do not call money, they don't officially have recycling conditions. Because they are constantly cutting, increasing and changing roles, however, you might say the essence of their work is continuously to recycle money to its greatest risk-adjusted usage.
 4. Simply how much will I be recharged?
4. Simply how much will I be recharged?
Exclusive equity and hedge resources both earn a yearly fee on possessions handled, usually 1% - 2per cent, including incentive charges typically amounting to 20% of profits. The combination of these management fees and incentive fees is where the oft-quoted “2 and 20” comes from.
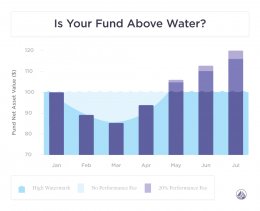
The time and triggers of motivation charges effect web returns and differ among investment kinds. Incentive settlement at hedge funds is usually driven by a concept known as an annual high-water mark, which will be various for each investor and reflects the net asset worth (NAV) of these share of fund at the time of their particular investment. Picture the rise and autumn of buyer's NAV as that of a literal line of liquid that leaves a mark in its aftermath. If you spend money on a fund at an NAV of $100 and it also later drops to $85 and then rises to $95, the high-water level of $100 can be viewed over the present $95 NAV and also the supervisor does not earn an incentive cost that 12 months (or previously, until it gets your NAV back above $100). If fund rises to $120, however, the manager is eligible for 20percent of $20, the total amount of NAV over the high water mark.
Private equity incentive charges, conversely, are usually based on a hurdle price, or minimal web return to the investor. If the challenge is 8percent annualized, like, an investor that experiences a 10per cent annualized return would be recharged 20percent of that whole 10%. If the return are at all below 8percent, however, the buyer will not be charged a reason charge on any percentage of the return. Because a fund could attain above-hurdle returns early in its life and disappoint later on, personal equity funds frequently have what are known as LP clawback terms wherein part or all a previously paid motivation charge is sent back towards the buyer's money account.
5. Whenever can I see my comes back?
Typically, the liquidity terms of a fund should match those of the fundamental opportunities. Consistent with hedge resources' typical concentrate on marketable securities, they tend to-be open-end funds, meaning that so long as discover capacity for more assets in a specific strategy, investors can invest or redeem cash within the investment's exchangeability parameters. Some resources permit money withdrawal each and every day, some restrict it to monthly, when one fourth, annually, or less, often according to the liquidity regarding the fundamental assets. Practically speaking, if a fund has actually performed really and you have held the investment during your lockup period, you'll get with sufficient advance notice and pocket the profits (minus relevant fees). If fund has done poorly, conversely, you'll redeem and reinvest the profits in something else.
On the other end of range, exclusive equity resources tend to be closed-end, reflecting their particular lasting investment in a lot less liquid possessions. Rather than take periodic assets and redemptions, exclusive equity businesses (categorised as sponsors) have actually a discrete money raise period per investment where they target a total investment size matching the range of the investment possibility set they intend to go after. Once the investment features often raised (or surpassed) its target (or tried and failed to do so over a maximum appropriate period of time ), the sponsor holds a final close. Following this happens, no extra capital is generally given accessibility the fund. All committed people tend to be locked into the fund before the end of their life in typically 8-12 years. PE's long-duration investments and matching closed-end construction are the operating forces behind the J-curve design to private equity returns.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE